Understanding Custom Attributes
What Are Custom Attributes?
With Custom Attributes in Divi 5, developers can seamlessly integrate HTML attributes into website elements, significantly enhancing accessibility and optimizing search engine performance. Unlock the full potential of your website and ensure a more inclusive user experience while improving your SEO results! Attributes such as alt, title, rel, and aria-label can be added to elements, enabling better interaction with assistive technologies and search engines.
Why Use Custom Attributes?
The implementation of Custom Attributes offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Accessibility: By adding attributes like
aria-label, you can provide additional context to screen readers, making your website more navigable for users with disabilities. Aria-labels are similar to alt text for images, which are added to image elements and serve the same purpose. - Improved SEO: Attributes such as
titleandaltcan help search engines understand the content of your images and links, potentially improving your site’s ranking. As an SEO company, Website Promoters knows this to be quite accurate. As an anecdote, one of our pages experienced a significant improvement in search rankings after updating the alt text of the images on the page to target specific keywords. - Greater Flexibility: Custom Attributes allow for more tailored functionality, enabling developers to create unique interactions and behaviors for different elements.
Getting Started with Custom Attributes
How to Add Custom Attributes
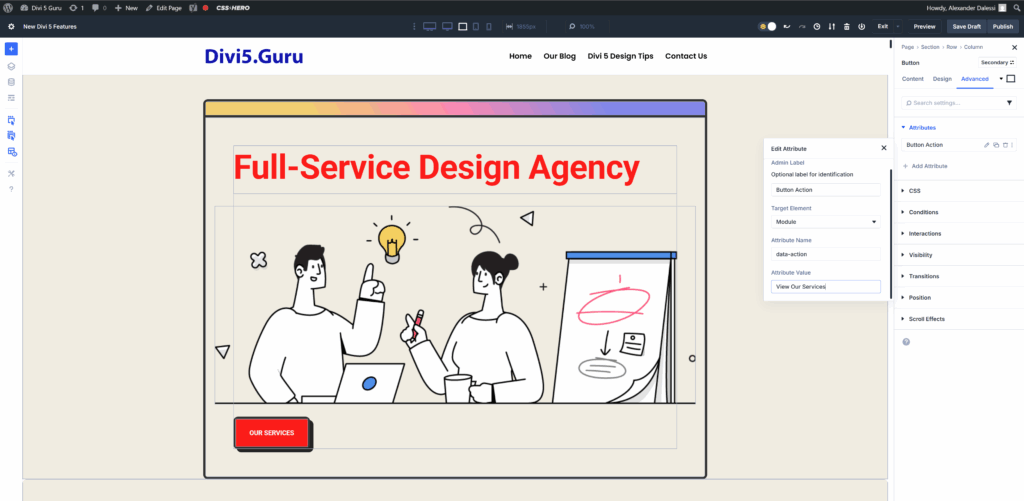
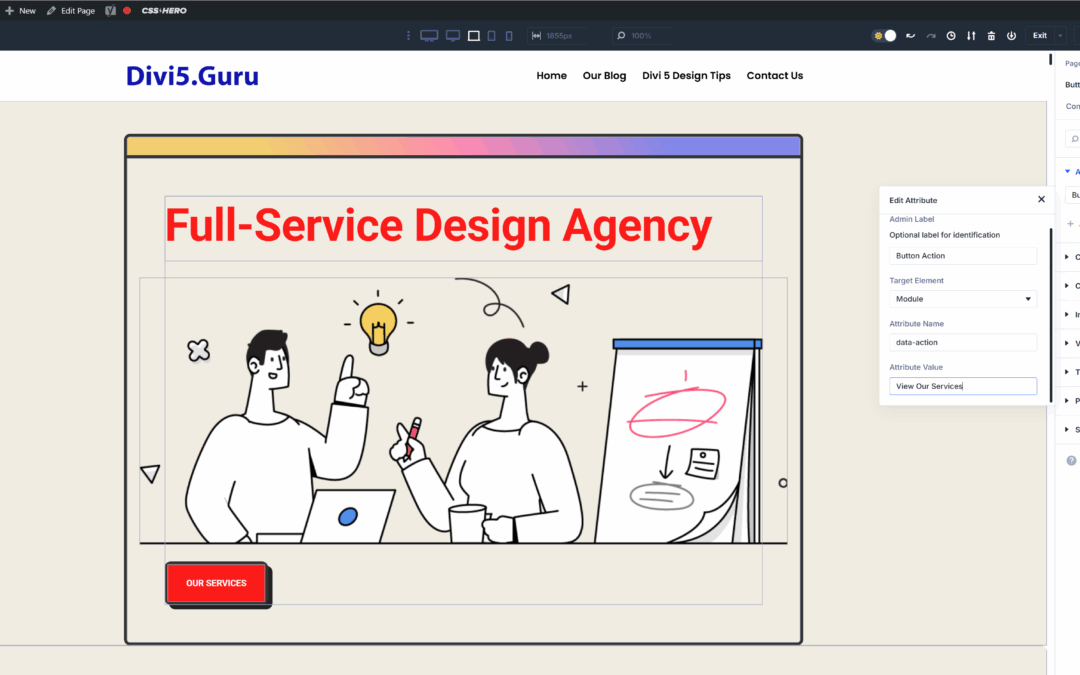
To add a custom attribute in Divi 5, select the module, go to the advanced tab, and click add attribute. Here, a data-action attribute is added to a button.
Adding Custom Attributes in Divi 5 is a straightforward process. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open the Divi Builder: Navigate to the page or post where you want to add Custom Attributes.
- Select the Module: Click on the module you wish to edit.
- Access the Advanced Tab: In the module settings, go to the “Advanced” tab.
- Add Attributes: In the “Attributes” section, you can enter your desired attributes. For example, to add an
altattribute to an image, you would enteraltas the name and provide the appropriate value.
Best Practices for Using Custom Attributes
To maximize the benefits of Custom Attributes, consider the following best practices:
- Be Descriptive: When adding attributes, ensure that the values are descriptive and relevant. This not only aids accessibility but also enhances SEO.
- Limit the Use of Attributes: While Custom Attributes are powerful, avoid overloading elements with too many attributes, as this can lead to confusion and clutter.
- Test for Compatibility: After adding Custom Attributes, test your website across different devices and browsers to ensure that everything functions as intended.
Practical Applications of Custom Attributes
Enhancing Image Accessibility
One of the most common uses of Custom Attributes is to improve the accessibility of images. By adding alt text, you provide context for users who cannot see the images. This is crucial for compliance with accessibility standards.
- Example: For an image of a sunset, you might use
alt="A beautiful sunset over the ocean".
Improving Link Functionality
Custom Attributes can also enhance the functionality of links. By using the rel attribute, you can specify the relationship between the current document and the linked document, which is particularly useful for external links.
- Example: For a link to an external site, you might use
rel="noopener noreferrer"to improve security and performance.
Customizing Button Behavior
Buttons are essential for user interaction, and Custom Attributes can be used to modify their behavior. For instance, adding a data-* attribute can help in tracking button clicks for analytics purposes.
- Example: You could add
data-action="subscribe"to a subscription button to track how many users click it.
Advanced Features of Custom Attributes
Utilizing Custom Attributes for Dynamic Content
With the introduction of dynamic content capabilities in Divi 5, Custom Attributes can be used to create more interactive and personalized user experiences. By linking attributes to dynamic content, you can tailor the information displayed based on user interactions.
- Example: You might use a
data-user-idattribute to personalize content for logged-in users.
Integrating with Third-Party Tools
Custom Attributes can also be integrated with third-party tools and plugins. This enables enhanced functionality and customization options, further improving the user experience.
- Example: If you are using a third-party analytics tool, you can add Custom Attributes to track user interactions more effectively.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Migration Challenges
As with any new feature, users may encounter challenges when migrating from previous versions of Divi. Some common issues include:
- Missing Attributes: Ensure that all necessary attributes are added during the migration process to avoid losing functionality.
- Compatibility Issues: Test your website thoroughly after migration to identify any compatibility issues with existing modules.
Debugging Custom Attributes
If you experience issues with Custom Attributes not functioning as expected, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check for Typos: Ensure that all attribute names and values are correctly spelled and formatted.
- Inspect Element: Use browser developer tools to inspect elements and verify that the attributes are being applied correctly.
Conclusion
Custom Attributes in Divi 5 represent a significant advancement in web design capabilities, offering enhanced accessibility, improved SEO, and greater flexibility. By understanding how to implement and utilize Custom Attributes effectively, you can create a more engaging and user-friendly website. As you explore the possibilities that Divi 5 offers, remember to keep accessibility and user experience at the forefront of your design strategy.
Sources
- Elegant Themes Documentation
- Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI)
- Search Engine Journal on SEO Best Practices